|  |
Temperature
Altitude Correction for Pressure Altitude
Pressure Altitude
QNH
QFE
Density Altitude
Coud Base
True Altitude
True Airspeed
Temperature Rise
Mach Number
Equivalent Airspeed
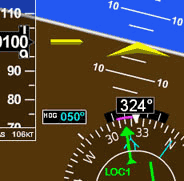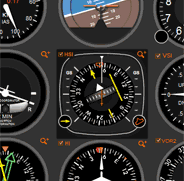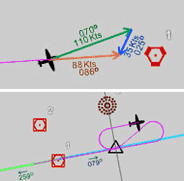
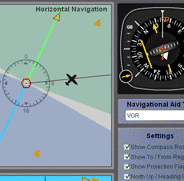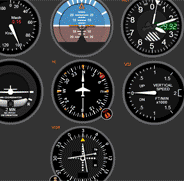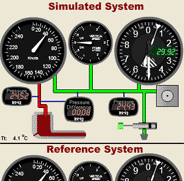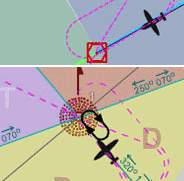
Magnetic Course
Magnetic Heading
Compass Heading
True Heading
Wind Triangle (TAS - HDG; GS - CRS; WS - WD)
Cross / Head Wind Components
Time - Speed - Distance
Fuel - Time - Fuel Flow
Surf with confidence! Site has been tested by: |
||
Miscellaneous | More functions than your average e6b: | |
| Calculators use multiple units for users of all countries |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
By Luiz Roberto Monteiro de Oliveira. Screenshots and video captures allowed (personal, business or military)
as long as credited to author and link to this site or URL included. Permission required for all other uses.
as long as credited to author and link to this site or URL included. Permission required for all other uses.